High-Performance PTFE Flat Seals
Application area
Almost universally usable (depending on pressure and temperature)
Not usable in alkali metals, elemental fluorine and chlorine trifluoride at high pressures
Product specification
Pure PTFE
Non-combustible
Excellent chemical resistance
Outstanding temperature resistance
Resistance: almost universal (see exceptions)
Technical specification
Material: PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene)
Color: white
Density: 2.14 - 2.19 g/m3 (DIN 53479-A)
Ball pressure hardness: 27 - 32 N/mm2 (DIN ISO 2039-1)
Tensile strength: 22 - 30 MPa (DIN EN ISO 527-2)
Elongation at break: 250 - 400 % (DIN EN ISO 527-2)
Tensile modulus: 350 - 750 MPa (DIN 53457)
Modulus of elasticity in bending: 600 - 800 MPa (DIN 53457)
Friction coefficient: 0.1 - 0.2 (dyn. against steel, dry)
Shore hardness D: 55° - 60° (DIN 53505)
Dielectric constant: 2.0 - 2.1 at 103 Hz and 106 Hz (DIN 53483)
Volume resistivity: >1018 Ohm x cm (ASTM D 257)
Thermal conductivity: 0.23 W/m * K (DIN 52612)
Coefficient of linear thermal expansion: 10 - 16 x 105/K (DIN 53752)
Oxygen index: >95 %
Water absorption: 0 % (ASTM D 570)
Temperature range: -200 to +260 °C
Melting point: +327 °C
General Information
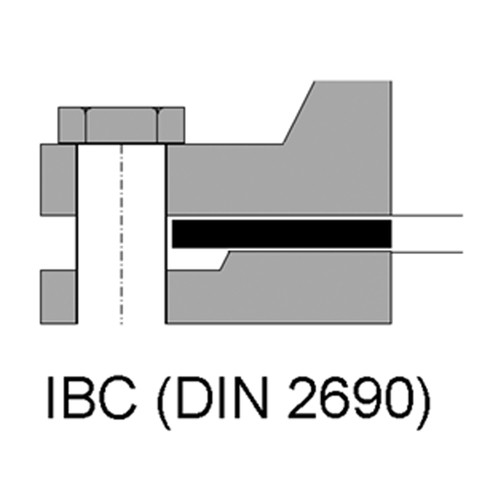
Flat seals are usually stamped as rings. For more complicated geometries, the rings are frequently cut by means of plotter or water jet. Rings are defined by the dimensions of the internal and external diameter as well as by the total thickness of the ring but often also by nominal diameter and pressure stage according to DIN 2690, 2691 (or 2692). For the purpose of harmonizing standards, these former flat seal standards are summarized in the EU standard DIN.
EN 1514-1. Still, the following sub-descriptions serve the purpose of illustrating the individual shapes: former DIN 2690: now EN 1514-1 Form IBC for smooth flanges; former DIN 2691: now EN 1514-1 Form TG for flanges with groove and tongue.
Advantages compared with other sealing elements:
symmetrical cross section, simple compact design, easy installation, wide selection of materials, grooving not required
Most common application: Flange sealing against liquid or gaseous media; static or quasistatic applications only.
Further applications: Housing and cover sealings.
Method of operation: The flat seal is axially pressed when mounting. The axial press force has to be greater than the sum of all radially acting forces to eliminate the risk of leakage. Cross-sectional leakage (the leakage diffused through the sealing material) is minimized by the selection of the right material. An optimal grouting of the flat seal prevents surface leakage, i.e. leakage occurring between flange and seal.
Materials for special requirements:
These flat seals are especially suited for use in processes that must comply with TA-Luft requirements.
Form IBC for smooth flanges: NW 10 to 200, PN 2.5 to 63
Form TG for flanges with groove and tongue: NW 10 to 200, PN 10 to 160
Manufacturing: according to the latest standards, with an optimal tool park, for quick and flexible handling, the traceability of materials is guaranteed, all parts go through a quality check before packaging.
| Item | Image | Design1 |
Innen-Ø mm
|
Außen-Ø mm
|
Höhe mm
|
NW mm
|
PN bar
|
Einheit Stück
|
Price Euro* | Buy |
|---|
Item
|
Image
|
Design1
|
Innen-Ø mm
|
Außen-Ø mm
|
Höhe mm
|
NW mm
|
PN bar
|
Einheit Stück
|
Price Euro* |
Buy
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 409200 |
|
IBC | 18 | 39 | 2 | 10 | 6 | 10 | 148.00 | |
| 409201 |
|
IBC | 18 | 39 | 2 | 10 | 6 | 20 | 252.00 | |
| 409202 |
|
IBC | 18 | 46 | 2 | 10 | 40 | 10 | 148.00 | |
| 409203 |
|
IBC | 18 | 46 | 2 | 10 | 40 | 20 | 252.00 | |
| 409204 |
|
IBC | 18 | 56 | 2 | 10 | 63 | 10 | 148.00 | |
| 409205 |
|
IBC | 18 | 56 | 2 | 10 | 63 | 20 | 252.00 | |
| 409206 |
|
IBC | 22 | 44 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 10 | 152.00 | |
| 409207 |
|
IBC | 22 | 44 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 20 | 260.00 | |
| 409208 |
|
IBC | 22 | 51 | 2 | 15 | 40 | 10 | 152.00 | |
| 409209 |
|
IBC | 22 | 51 | 2 | 15 | 40 | 20 | 260.00 | |
| 409210 |
|
IBC | 21 | 61 | 2 | 15 | 63 | 10 | 152.00 | |
| 409211 |
|
IBC | 21 | 61 | 2 | 15 | 63 | 20 | 260.00 | |
| 409212 |
|
IBC | 27 | 54 | 2 | 20 | 6 | 10 | 206.00 | |
| 409213 |
|
IBC | 27 | 54 | 2 | 20 | 6 | 20 | 350.00 | |
| 409214 |
|
IBC | 27 | 61 | 2 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 206.00 | |
| 409215 |
|
IBC | 27 | 61 | 2 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 350.00 | |
| 409216 |
|
IBC | 25 | 72 | 2 | 20 | 63 | 10 | 206.00 | |
| 409217 |
|
IBC | 25 | 72 | 2 | 20 | 63 | 20 | 350.00 | |
| 409218 |
|
IBC | 34 | 64 | 2 | 25 | 6 | 10 | 250.00 | |
| 409219 |
|
IBC | 34 | 64 | 2 | 25 | 6 | 20 | 416.00 | |
| 409220 |
|
IBC | 34 | 71 | 2 | 25 | 40 | 10 | 250.00 | |
| 409221 |
|
IBC | 34 | 71 | 2 | 25 | 40 | 20 | 416.00 | |
| 409222 |
|
IBC | 30 | 82 | 2 | 25 | 63 | 10 | 250.00 | |
| 409223 |
|
IBC | 30 | 82 | 2 | 25 | 63 | 20 | 416.00 | |
| 409224 |
|
IBC | 43 | 76 | 2 | 32 | 6 | 5 | 196.00 |